
The angle bisector of the triangle is perpendicular to the side with different length. The angle bisector divides the unequal angle into equal half. Note: In isosceles triangle the two sides are equal and the two angles corresponding to the sides are equal. $\therefore $ proved the converse Isosceles Triangle Theorem. Converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem. As a result, we may identify an isosceles. These two congruent sides are called the legs of the triangle. Corollary 3: The bisector of the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle is perpendicular to the base at its midpoint. The isosceles triangle theorems converse states that a triangle with two equal angles will have two equal sides. By definition, a triangle that has two congruent sides is an isosceles triangle.

In this problem, you are applying the converse, which is also true : If. Since corresponding part of congruent triangles are congruent, so the two sides of the triangle will be equal, which is Answer In this triangle, we can observe that there are two sides of equal length: the lengths of and are both given as 2 cm. The isosceles triangle theorem states that when two sides of a triangle are. So by the$AAS$ property of triangle the two triangle $\vartriangle ABD$ and $\vartriangle ACD$ are congruent. In both the triangles $\vartriangle ABD$ and $\vartriangle ACD$ the line segment $AD$ which is also the angle bisector of $\angle A$ is common. Hypotenuse-Leg Congruence Theorem CPCTC Isosceles Triangle Base Angle Theorem Isosceles Triangle Base Angle Converse Isosceles Triangle Base Theorem. cosCcosA + sinCsinAcosb -cosBcosA + sinBsinAcosc.
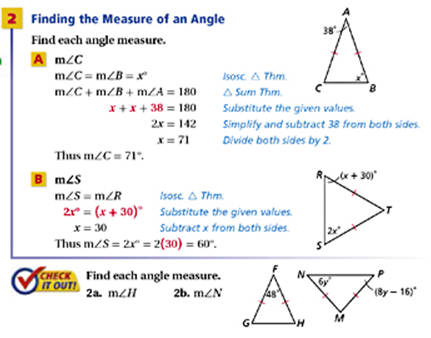
As I know they are equal, I made the equations equal and worked from there. Conversely, if the base angles of a triangle are equal, then the triangle is isosceles. These two angles are equal because the line $AD$ which was constructed is a bisector of the angle $\angle BAC$. begingroup What Ive done is used the cos rule for cosB and cos C (as angles B and C are in my triangle ABC). In an isosceles triangle, the angles opposite to the equal sides are equal. These angles are equal as stated in the theorem. The three properties which make the triangle $\vartriangle ABD$ and $\vartriangle ACD$ congruent are The proof is very quick: if we trace the bisector of C that meets the opposite side AB in a point P, we get that the angles ACP and BCP are congruent. In this section, we will take a look at examples related to isosceles triangle theorem.

If two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite those angles are congruent. \) resembles a bridge which in the Middle Ages became known as the "bridge of fools," This was supposedly because a fool could not hope to cross this bridge and would abandon geometry at this point.Now, on analysing the above triangle we see that the triangle could be proved congruent. The converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem states that if two angles A and B of a triangle ABC are congruent, then the two sides BC and AC opposite to these angles are congruent. The converse of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem is also true.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
